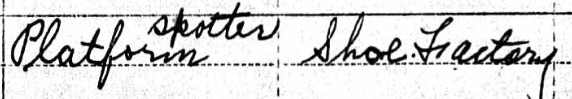As we saw, Friederike Blumenfeld Schoen had five children. They all had their lives and destinies changed by the Holocaust. Her oldest child Jakob died in 1937, and his widow and daughter were killed in the Holocaust. Friederike’s second oldest son, Moritz, immigrated with his family to the US in the late 1930s to escape the Nazis.
The other two surviving children of Friederike Blumenfeld Schoen, Auguste and Isaak, ended up in Shanghai, China, during the war. I don’t have any details about how they got to Shanghai or what their lives were like there, but there have been many books1, articles2, and memoirs3 written about the experience of Jewish refugees in Shanghai, and there was even an exhibit about Jewish refugee life in Shanghai in August 2023 in New York City.
I have read some of the articles, but not the books, so I can only briefly touch on the outline of this period in history to give context to what happened to Auguste, her husband Willi, their son Julius, and her brother Isaak, but in the footnotes I have listed sources for those who may want to learn more about the Shanghai Jewish community during the Nazi era.
When I first heard many years ago that Shanghai had been a place that many Jews sought refuge during the Nazi era, I was surprised. I’ve since learned that there was in fact a small Jewish community in Shanghai even before the 1930s, most of whom had fled from Russia after the Russian Revolution in 1917. But it was not until the 1930s that the Jewish population in Shanghai grew to about 20,000 refugees. Why Shanghai? One reason was that unlike most other places in the world including the United States, no visas were required to enter Shanghai until August 1939.4
In 1937, after a fierce battle with the Chinese, the Japanese took control of large sections of Shanghai and created a ghetto in a section called Hongkew, where Jewish refugees lived in poverty-stricken conditions. They were not allowed to leave or enter the ghetto without passes and were often mistreated by the Japanese officials who oversaw the ghetto. The Chinese residents of Shanghai also were persecuted and suffered greatly during this occupation, which lasted until the end of World War II when Japan was defeated and required to leave China.5

Jewish Ghetto Memorial in Shanghai, gruntzooki, CC BY-SA 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
I wish I knew more about the experiences of my relatives Auguste Schoen Speier and her family and her brother Isaak Schoen in Shanghai, but aside from finding their names on various lists and in a 1939 directory for Shanghai located by Richard Bloomfield, I know no details other than that at some point they arrived there from Germany and lived there until after the war.
Auguste, Willi, and Julius Speier and Isaak Schoen are all listed on a 1950 list of Jewish refugees in Shanghai who were helped by the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee, an organization that continues to exist today for those in need.
I also found them all here in a collection of records of Shanghai refugees made in 1944.
Richard located them in this November 1939 directory of emigrants in Shanghai, so obviously they had immigrated there by November 1939:
But I could not locate them on this list of refugees who had arrived in Shanghai between 1937 and 1944, so perhaps they had arrived before 1937.
In his interview with the US Holocaust Memorial and Museum, Kurt Schoen, Moritz’s son, mentioned that one of his cousins had died from typhoid while living in Shanghai, but I have no record or even a name of that cousin. He or she does not appear on any of the lists cited above. Maybe that cousin had passed away before these lists were compiled. Or maybe Kurt was confused.6
In any event, it is clear that Auguste, Willi, Julius and Isaak all ended up in Shanghai, and then after the war, they all immigrated to the US.
Auguste’s son Julius was the first to make it to the US. He arrived in San Francisco on March 19, 1947, with his wife Hildegarde Gabriel. They had married in Shanghai on December 9, 1945.7 Hildegarde was the daughter of Julius Gabriel and Berta Gross and was born on September 8, 1919, in Bromberg in what was then part of Prussia but is now in Poland.8
On the ship manifest, Julius listed his father Willi as the person he was leaving behind, Hildegarde listed her father Julius. They both listed Moritz Schoen, Auguste’s brother, as the person they were going to in the US and listed their destination as New York City. Julius listed his occupation as a shoemaker, and Hildegarde listed hers as a nurse.
Julius and Hildegarde Speier ship manifest, he National Archives at Washington, D.C.; Washington, D.C.; Passenger Lists of Vessels Arriving At San Francisco, California; NAI Number: 4498993; Record Group Title: Records of the Immigration and Naturalization Service, 1787-2004; Record Group Number: 85, NARA Roll Number: 388, Ancestry.com. California, U.S., Arriving Passenger and Crew Lists, 1882-1959
Julius’ parents Auguste (Schoen) and Willi Speier arrived in San Francisco six months later on September 24, 1947. The ship manifest indicates that they were headed to New York City where their son Julius was residing. Like his son Julius, Willi was a shoemaker or “cobbler,” as listed on the manifest. The person they were leaving behind in Shanghai was Auguste’s brother Isaak.9
Isaak himself arrived just a few months later on December 17, 1947. He also entered the US in San Francisco, indicating that he also was heading to New York City where his brother Moritz was living. He listed his occupation as a salesman.10
Auguste and Willi did end up in New York City, where in 1950 Willi was working as a “platform spotter” in a shoe factory. I don’t know what that means, but I would guess that it means he watched shoes on an assembly line. If anyone has any other ideas, please let me know.11 I’ve been unable to locate their son Julius and his wife Hildegarde on the 1950 census nor can I locate Isaak Schoen on that census.
Thus, three of Friederike Blumenfeld and Mannes Schoen’s children and four of their grandchildren had escaped Nazi Germany and survived World War II. Their lives after 1950 will be discussed in my next post.
- See, e.g., Alex Ross, Escape to Shanghai: A Jewish Community in China (1993, Free Press); Gao Bei, Shanghai Sanctuary: Chinese and Japanese Policy Toward European Jewish Refugees During World War II (2016, Oxford University Press); Irene Eber, Wartime Shanghai and the Jewish Refugees From Central Europe: Survival, Co-Existence, and Identity in a Multi-Ethnic City (2012, DeGruyter). ↩
- See, e.g., the articles at the following links: https://www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/how-holocaust-survivors-found-refuge-shanghai-told-through-stories-and-photos-180978235/ and https://www.nbcnews.com/news/asian-america/jewish-wwii-refugees-found-safety-shanghai-are-focus-new-exhibit-rcna96478 and https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/article/german-and-austrian-jewish-refugees-in-shanghai and https://www.npr.org/2023/08/06/1192118339/jewish-refugees-shanghai-world-war-ii ↩
- E.g., Ernest Heppner, Shanghai Refuge: A Memoir of the World War II Jewish Ghetto (1995, University of Nebraska Press); Berl Falbaum, ed., Shanghai Remembered…: Stories Of Jews Who Escaped To Shanghai From Nazi Europe (2005, Momentum Books, LLC.); Sigmund Tobias, Strange Haven: A Jewish Childhood in Wartime Shanghai (2009, University of Illinois Press). ↩
- See Note 2, above. ↩
- See Note 2, above. ↩
- Kurt L. Schoen, July 24, 2004 interview, Accession Number: 1997.A.0441.512 | RG Number: RG-50.462.0512, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum Collection, Gift of the Gratz College Holocaust Oral History Archive, found at https://collections.ushmm.org/search/catalog/irn566135. There was another puzzling thing about Kurt’s interview. He mentioned that his father had one sister (Auguste) and one unmarried brother (Isaak), but did not mention Jakob, his father’s older brother. Jakob, as we saw, had died in 1937 when Kurt was ten, and his wife and daughter were killed in the Holocaust. Had Kurt never known his uncle Jakob and his family? Had Moritz never mentioned them? Or was it just too painful for Kurt to talk about what had happened to his uncle, aunt, and cousin? ↩
- Marriage notice for Julius Speier and Hildegarde Gabriel, The Jewish Voice in Jüdisches Nachrichtenblatt, 23. November 1945, p. 8 ↩
- Hildegard Speier, Gender Female, Race White, Birth Date 8 Sep 1919, Birth Place Bromberg Pos, Federal Republic of Germany, Death Date Aug 1994, Father Julius Gabriel, Mother Berta Gross, SSN 079242443, Ancestry.com. U.S., Social Security Applications and Claims Index, 1936-2007 ↩
- Willi and Auguste Speier, ship manifest, The National Archives at Washington, D.C.; Washington, D.C.; Passenger Lists of Vessels Arriving At San Francisco, California; NAI Number: 4498993; Record Group Title: Records of the Immigration and Naturalization Service, 1787-2004; Record Group Number: 85, NARA Roll Number: 392, Ancestry.com. California, U.S., Arriving Passenger and Crew Lists, 1882-1959 ↩
- Isaak Schoen ship manifest, The National Archives at Washington, D.C.; Washington, D.C.; Passenger Lists of Vessels Arriving At San Francisco, California; NAI Number: 4498993; Record Group Title: Records of the Immigration and Naturalization Service, 1787-2004; Record Group Number: 85, Ancestry.com. California, U.S., Arriving Passenger and Crew Lists, 1882-1959 ↩
- National Archives at Washington, DC; Washington, D.C.; Seventeenth Census of the United States, 1950; Year: 1950; Census Place: New York, New York, New York; Roll: 4546; Page: 18; Enumeration District: 31-1702, Ancestry.com. 1950 United States Federal Census ↩