Although I had a fairly easy time locating the names, birth dates, marriages, and children of the five children of Meier Rothschild and Bertha Lorge and I knew that all five lived beyond World War II, I have had a much harder time finding information about how they survived the Holocaust—did they leave in time or did they get sent to the camps? And where did they go after the war?
Each of those five children presented some research challenges because it appears that none of them ended up in the same place and almost all ended up somewhere other than the United States. So the records are harder to locate—if they exist at all. But I will do my best to trace their histories during the 1930s and thereafter.
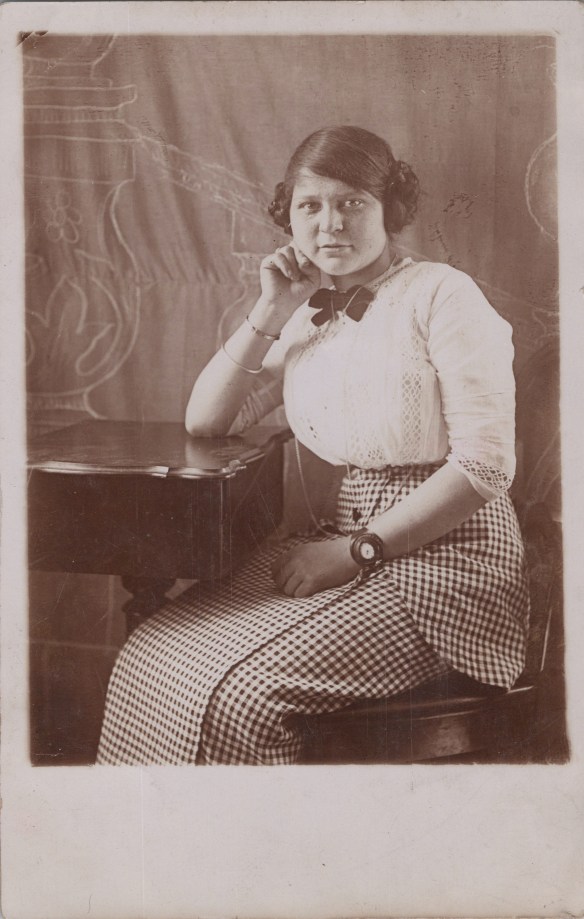
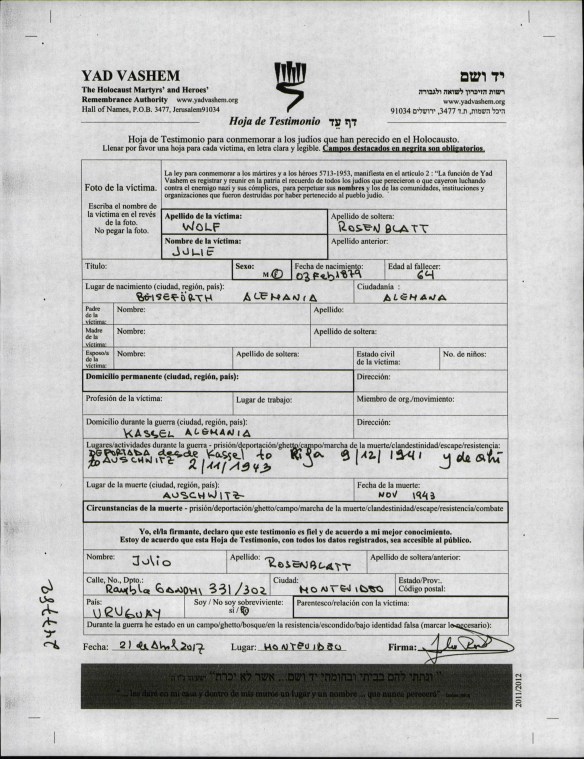
Starting with the oldest child, Berthold Rothschild, his wife Sarah Adler, and their daughter Adelheid, one fact I was able to establish was that Sarah died on May 15, 1937, when she was only 43. The death record says she died in Herborn, which is a small town about 60 miles from Frankfurt, where the death record states she was living. So why was she in Herborn and not Frankfurt where Berthold lived? What caused her death? Was it related to the persecution of Jews by the Nazis? I didn’t know.

Sarah Rotschild, Maiden Name Adler, Gender weiblich (Female), Death Age 43, Birth Date Abt 1894, Death Date 15 Mai 1937 (15 May 1937), Death Place Herborn, Hessen (Hesse), Deutschland (Germany), Civil Registration Office Herborn, Certificate Number 74, Hessisches Hauptstaatsarchiv; Wiesbaden, Deutschland; Personenstandsregister Sterberegister; Bestand: 4139; Laufende Nummer: 911, Ancestry.com. Hesse, Germany, Deaths, 1851-1958
I thought that perhaps there was more information in the parts of the death record that I could not read and asked in the GerSIG group on Facebook for help. Ralf, a member there, provided me with this translation:
The management of the state sanatorium has announced that Sara Rothschild, née Adler, without occupation, 43 years old, resident of Frankfurt am Main, born in Rüsselsheim, district of Gross-Gerau, divorced, died in the state sanatorium in Herborn on the afternoon of the fifteenth of May 1937 at five and a half o’clock.
I added the emphasis to two parts here. First, Sarah’s marital status was reported as divorced. I went back to the marriage record for Berthold and Sarah and now saw there was a marginal comment that in fact says that they were divorced as of May 22, 1934.

From the marriage record of Berthold Rothschild and Sarah Adler, Hessisches Hauptstaatsarchiv; Wiesbaden, Deutschland; Bestand: 903
Source Information
Ancestry.com. Hesse, Germany, Marriages, 1849-1930
Then I looked a little further and learned that there was (and is) a psychiatric hospital in Herborn known then as Landesheil- und Pflegeanstalt Herborn (State Healing and Nursing Institution Herborn). I was disgusted when I learned that this hospital was a place used by the Nazis for forced sterilization; 561 women and 623 men were forcibly sterilized, many after a diagnoses of “feeblemindedness.” Patients slept on straw sacks instead of mattresses. Later, after Sarah’s death, Jewish patients were deported from the hospital to the concentration camps. I don’t know what circumstances caused Sarah to be sent to Herborn, but I imagine that the conditions there and the Nazi control of the facility were factors in her early death at 43.
As for her ex-husband Berthold, I have not been able yet to locate his whereabouts before 1943. As seen below, I know that in 1943 he was living in Port Elizabeth, South Africa, and in 1957 he traveled from Port Elizabeth, South Africa, to England, reporting that he was a photographer. The passenger manifest indicates that he planned to stay in England permanently.1
But he died on May 17, 1964, in Port Elizabeth, South Africa, not in England. The death certificate reported that he was a photographer, a widower, and wanted to be buried in Jerusalem, Israel. Unfortunately, I have not found any further information yet. I don’t know when he left Germany, when he ended up in South Africa, or anything else about his life between his divorce in 1934 and his travels in 1959 and then his death in 1964.

Berthold Rothschild death certificate, “South Africa, Civil Death Registration, 1953-1967”, FamilySearch (https://www.familysearch.org/ark:/61903/1:1:6Z3Z-F3SN : Wed Jan 15 15:31:44 UTC 2025), Entry for Berthold Rothschild, 17 May 1964.
As for Berthold and Sarah’s daughter Adelheid, I also only have random pieces of information about her life. I have inferred that she was sent to Westerbork sometime during the Nazi era—that is, the detention camp outside of Amsterdam where Jews were sent before being transported to the death camps. A record on the WieWasWie site includes the marriage certificate of Adelheid Rothschild and Manfred Samson. They were married on November 22, 1943, in the Westerbork camp.

Marriage record for Adelheid Rothschild and Manfred Samson, found at https://www.wiewaswie.nl/nl/detail/111087321
I asked ChatGPT, having been told that AI can be helpful on translations, to transcribe and translate this marriage record. And this is a warning to anyone else who relies on ChatGPT for this type of inquiry. It made several errors. This was the first translation it produced.
Record No. 116. On Thursday, 23 December 1943, before me, Registrar of Civil Status of the municipality of Westerbork, appeared for the purpose of entering into marriage:
Manfred Samson, aged 29, merchant, born in Leipzig, Germany, residing in Westerbork, son of Sami Samson and Berta Samson, both residing in Bielefeld.
Adelheid Rothschild, aged 29, without occupation, born in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, residing in Westerbork, daughter of Siegfried Rothschild, merchant, residing in Port Elizabeth, South Africa, and Paula Rothschild, without occupation, residing in Baden.
After the required announcements and with no impediment having appeared, they declared that they accepted one another as husband and wife.
I knew that the information in bold could not be correct. On the WieWasWie page itself, it had different information based on the same record. After several inquiries about this to ChatGPT, it admitted it had read the handwriting incorrectly and made the changes. The translation now reads:
Manfred Samson, aged 19, merchant, born in Leipzig, Germany, residing in Westerbork, son of Josef Samson and Zerlina Hoelzer, both residing in Bielefeld.
Adelheid Rothschild, aged 22, without occupation, born in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, residing in Westerbork, daughter of Siegfried Rothschild, merchant, residing in Port Elizabeth, South Africa, and Sarah Adler, deceased.
Thus, a word of caution to those relying on ChatGPT or any other AI tool for transcribing records: DO NOT TRUST THEIR WORK!!!
But one thing that I did learn from the translation is that Berthold was already in South Africa in 1943 when his daughter Adelheid was married in Westerbork. Why had she gone to the Netherlands instead of to South Africa with her father? I wish I knew.
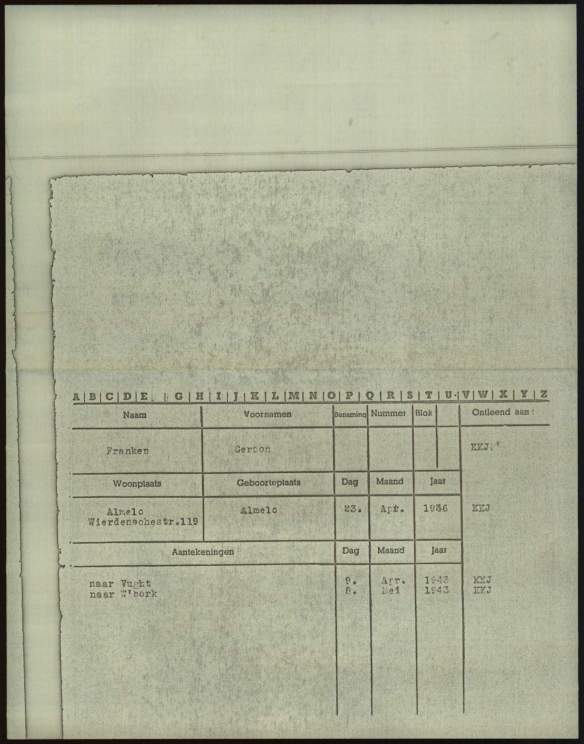
Manfred Samson was born on December 2, 1923, in Leipzig and was a student of agriculture and horticulture.2 A record in the Arolsen Archives indicates that Manfred left Leipzig for Holland on November 28, 1938. He was sent to Westerbork on November 7, 1942.3

Manfred Samson registration as Jew in Leipzig, Arolsen Archives, 7 Archival records of microforms (new material / document acquisition) / 7.5 Document acquisition in Germany / 7.5.4 Leipzig, Archiv der Israelitische Religionsgemeinde /Mitgliederkartei, Reference Code
754003
Other Arolsen Archives records, one for Manfred and one for Adelheid, both contain the notation “BB 11.1.44,” I wondered whether that meant that Adelheid and Samson were deported to Bergen Belsen on January 11, 1944.

Manfred Samson, Arolsen Archives, 1 Incarceration Documents / 1.2 Miscellaneous / 1.2.4 Various Organizations /Documents with names from SALOMONS, Eva, Reference Code
01020402 220

Adelheid Samson Arolsen Archives, 1 Incarceration Documents / 1.2 Miscellaneous / 1.2.4 Various Organizations /Documents with names from ROSIANSKI, Jozef, Reference Code
01020402 217
Fortunately both Adelheid and Manfred survived the camps. They are both listed on several documents created after the war by the Joint Distribution Committee that identify Jews who were liberated from the Celle/Frankfurt an der Oder camp.4
I had never heard of this camp before but learned that it was located eleven miles north of Bergen-Belsen, so that reinforces my assumption that BB stood for Bergen Belsen and that Celle was just another way of referring to Bergen-Belsen or a satellite camp nearby.
For a long time I could find no clue as to where Manfred and Adelheid went after being liberated from the camp. Then I saw the reverse of one of the Arolsen Archives documents and noticed this:

Manfred Samson, Arolsen Archives, 7 Archival records of microforms (new material / document acquisition) / 7.5 Document acquisition in Germany / 7.5.4 Leipzig, Archiv der Israelitische Religionsgemeinde /Mitgliederkartei, Reference Code 754003
From this document it appears that Manfred (and perhaps Adelheid) ended up in a kibbutz in Israel. But I haven’t found any other records for them on either the IGRA website or the Israel State Archives website. Kibbutz Schluchoth was the first kibbutz created after the formation of the State of Israel, according to their website, and was founded primarily by Holocaust survivors from Germany and Austria. I sent them an email asking if they had information about Manfred and Adelheid Samson, but have not received a response.
It took hours of work to string together this information about Berthold and his family, and I wish I knew more. But perhaps the biggest lesson I learned from this research is NOT to rely on ChatGPT to transcribe and translate documents accurately.
- Berthold Rothschild, passenger manifest, The National Archives in Washington, DC; London, England, UK; Board of Trade: Commercial and Statistical Department and Successors: Inwards Passenger Lists; Class: Bt26; Piece: 1382; Item: 67, Month: Jun, Ancestry.com. UK and Ireland, Incoming Passenger Lists, 1878-1960 ↩
- Arolsen Archives; Bad Arolsen, Germany; Record Group 1 Incarceration Documents; Reference: 1.2.4.2, Ancestry.com. Germany, Incarceration Documents, 1933-1945; https://www.wiewaswie.nl/nl/detail/111087321 ↩
-
Arolsen Archives, 1 Incarceration Documents / 1.2 Miscellaneous / 1.2.4 Various Organizations /Documents with names from SALOMONS, Eva, Reference Code
01020402 220 ↩ - E.g., Adelheid Samson, Manfred Samson, Arolsen Archives; Bad Arolsen, Germany; Registration of Liberated Former Persecutees at Various Locations (F18 lists); Reference: DE ITS 3.1.1.3 DE, Reference Number: 008804350, Ancestry.com. Registration of Liberated Former Persecutees, 1945-1950 ↩