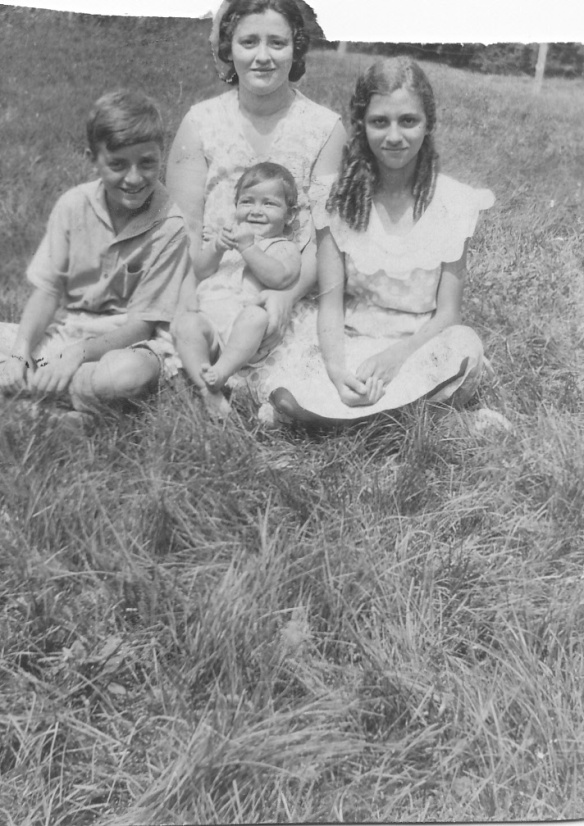
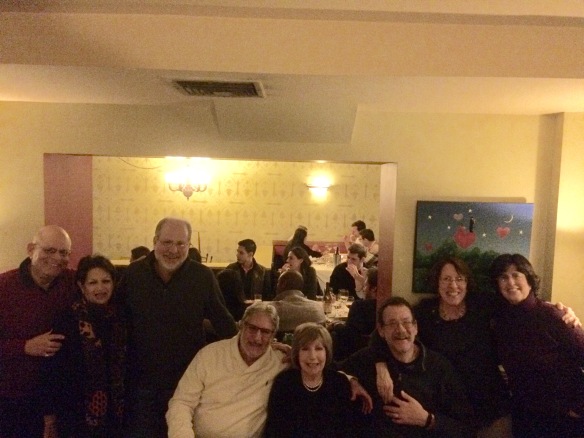
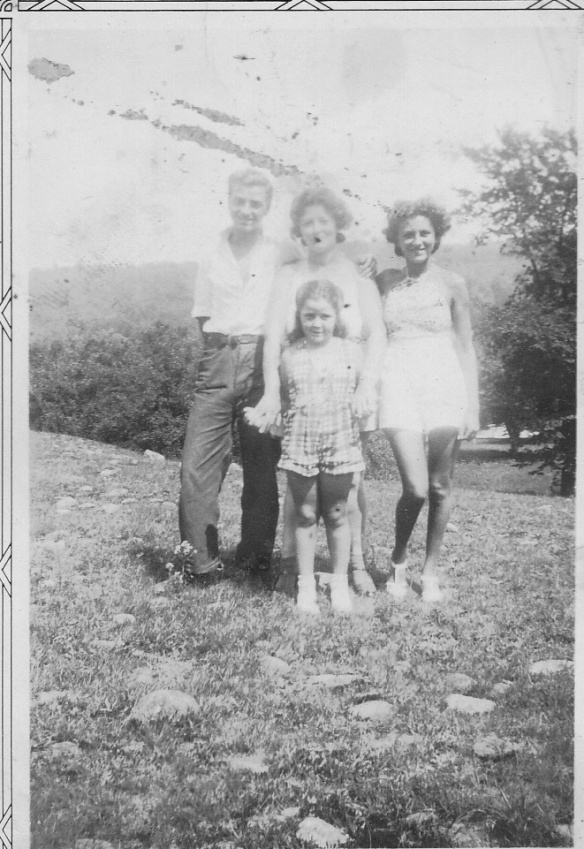Among the other treasures that turned up in the shoebox of “old papers” that had belonged to my Aunt Elaine was a Martinson Coffee pocket calendar for the year 1930. My aunt would have been twelve going on thirteen, my Uncle Maurice ten going on eleven, and my mother not yet born when 1930 began. Here’s a photograph of my grandmother and her three children taken in 1931 when that pocket calendar was still relatively new:
This calendar, however, had to be around for many years as a place where members of the family scribbled notes of all kinds because even my mother eventually made contributions to it. In fact, the most recent entries seem to have been made by my grandmother in 1965 long after my grandfather had died and all her children had married.
I don’t know for sure what “Johen” meant, but I wonder if my grandmother was referring to my father, whose name is John Cohen.
It amazes me that my grandparents kept this little book for so long, and I wonder why it became the repository of so many family notes. I can’t imagine how it stayed around and was used by so many members of the family beginning in 1930 up to 1965. Today that notebook probably would not have lasted a year (well, it wouldn’t exist since we’d use our smartphones and computer calendars instead.)
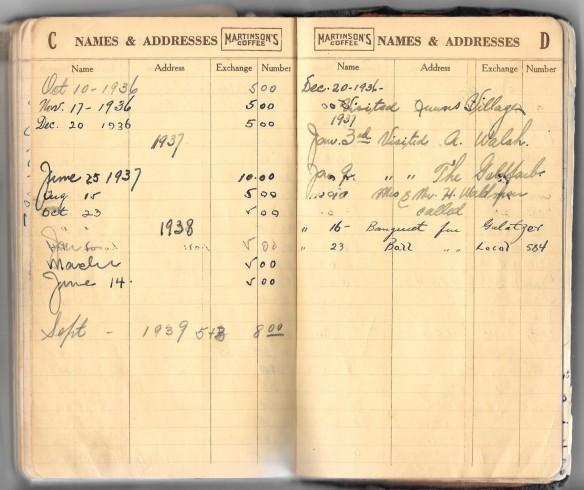
For example, my grandparents used it not only as a calendar but as an address book. I already posted two of the pages of addresses in an earlier post:
Here are a few more:
Leo Ressler was my mother’s first cousin, son of Tillie Brotman Ressler, my grandmother’s sister. His wife was Mildred Phillips, and the notebook page records both their wedding anniversary and Mildred’s birthday. Unfortunately there is no year given for the marriage, but Mildred was still single and living with her mother and stepfather in New Haven, Connecticut, on the 1930 census. She and Leo lived in Hartford during the late 1930s, and so this entry of an address for Bridgeport must have been long after the 1930 date on this calendar. (They were living in Bridgeport as of the 1940 US census.) Leo and Mildred owned a dress shop in Connecticut for many years before retiring to Florida. My mother recalls that Mildred was considered high class by my grandparents and that my aunt was invited to come visit them so she could learn some of Mildred’s sophisticated ways.
(I don’t know who Francis Coen would be— another name to research.)
The next two pages had three addresses for my mother’s uncle, Sam Brotman—my grandmother’s brother. Apparently he moved around a bit, given all the crossed out addresses the notebook includes for him. (There are two more on the first page, above.) I don’t know very much about Uncle Sam except that he was a cab driver and lived alone all his adult life. Yet all these addresses include a “in care of” reference so perhaps he was living with someone named Weinstein for some period of time and someone named Enzer at other times.
Joe Brotman, the other name on this page, was another of my mother’s first cousins, the son of Hyman Brotman, my grandmother’s brother. I have six different Joseph Brotmans in my family tree, including my great-grandfather, but Hyman’s son is the only one who lived in Queens, where he was living when this address was recorded.
My grandfather also used the calendar to record birthdays for family members. There are notes on the dates for his birthday as well as that of my grandmother, my aunt, and my mother. (The pages for June were torn out, so there is none for my uncle.) My mother was born during 1930, and on the appropriate date my grandfather simply wrote, “My daughter’s birthday, Florence, born—-.”
One of my favorite pages (although very hard to read) is the one where my grandfather apparently listed all his favorite pieces of music. I know that music was one of his passions, one of the few things he remembered fondly about his childhood in Iasi, Romania:
I can’t make out the names of most of the pieces, but he has works by Beethoven (whose name he wrote with such a flourish on the opposite page), Brahms, Bizet, and Grieg as well as several others.
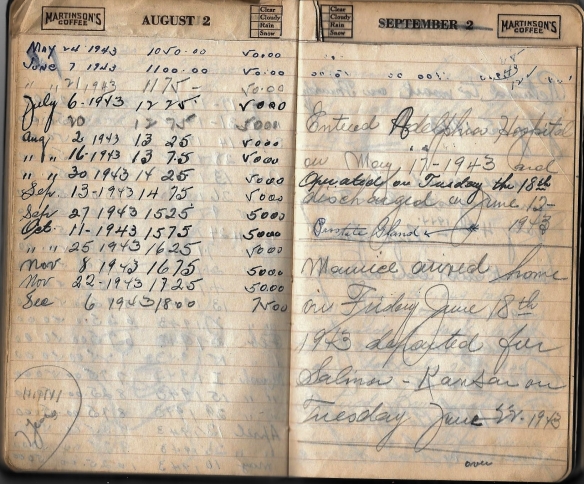
He also used the notebook as an account book, and there are many pages where he records his paychecks, his Social Security benefits, and Welfare Fund payments. My grandfather was active in his union, and I assume that the Welfare Fund was administered by the union. In addition, he kept a record of people they visited or who visited them and other events.
The notebook also contains a number of notes my grandfather made about his health and various other matters. For example, on these pages he not only recorded financial information; he interspersed notes about the times my uncle came home to visit during his military service in World War II with notes about his own operations and hospitalizations.
Again, all of these were obviously written long after 1930 and as late as 1951 when he had surgery for polyps. He died just six years later on May 3, 1957.
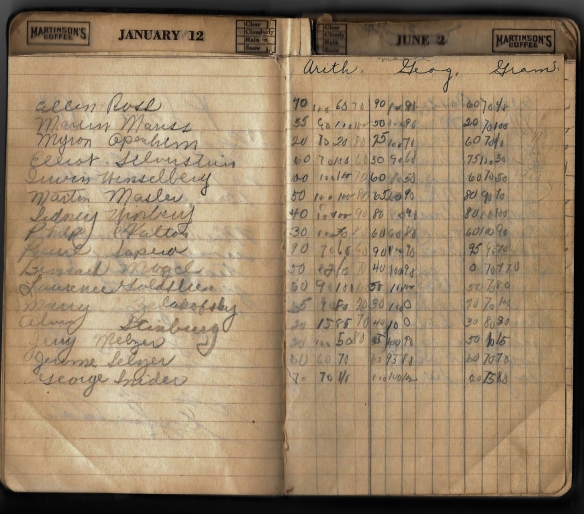
But perhaps the most interesting and entertaining parts of the notebook are those contributed by my aunt, my uncle, and my mother. There are many pages like this one with a list of names and then what looks like grades. My mother believes that my aunt used the notebook to play school, listing her classmates and even her brother and herself as the students and then “grading” them in different subjects.
My aunt also liked to practice writing her name and doodling all over the pages (the top one might have been written by my mother or someone else; I am not sure):
These pages were obviously written after my aunt was married as she used her married name (Lehrbaum) and included her husband, my Uncle Phil. The second page also includes my uncle’s wife, my Aunt Lynn, and they weren’t married until 1945, several years after Aunt Elaine had married. I find it fascinating that even after she was married and out of the house, my aunt still somehow found this notebook a place to scribble.
I found the pages my uncle wrote in 1934 about his adventures shooting at chipmunks, squirrels, and rabbits with his friend Blackie both amusing and disturbing. First, the idea that my uncle was carrying around a real gun at age fifteen is rather horrifying. Secondly, I always knew my uncle as an animal lover. He always had a dog (a schnauzer named Schnopsie is the one I remember best), and later on he had several dogs and cats as well as various other animals. How could he shoot harmless chipmunks, squirrels, and rabbits? But when I asked my cousin Beth about this, she said he always liked to shoot, so she was not surprised.
But it’s amusing also because I can imagine my uncle as a fifteen year old boy having a wild time with his friend Blackie and competing to see who would shoot the most animals that summer. Below is a photo of my uncle, my aunt, and my mother as well as my grandmother about a year after the summer that my uncle was writing about his hunting adventures.
I found the note he wrote four and a half years later on February 24, 1939, when he was almost twenty years old particularly touching and revealing:
As I recall it now I have recorded on these last nine pages possibly one of the happiest phases of my life. As I sit here and look back four and a half years it seems incredible that time could fly by so quickly on the wings of joy and sorrow, (yes, we’ve had our share of sorrows).
What were those sorrows? I don’t know what my uncle was referring to specifically or whether he only meant between 1934 and 1939, but in his lifetime, in 1924 his aunt Frieda had died after childbirth as had her baby; his aunt Tillie had lost her husband Aaron, and his grandmother Bessie had died in May 1934, shortly before he wrote about his hunting adventures. I also imagine that those Depression years were challenging for my grandparents like they were for so many people.
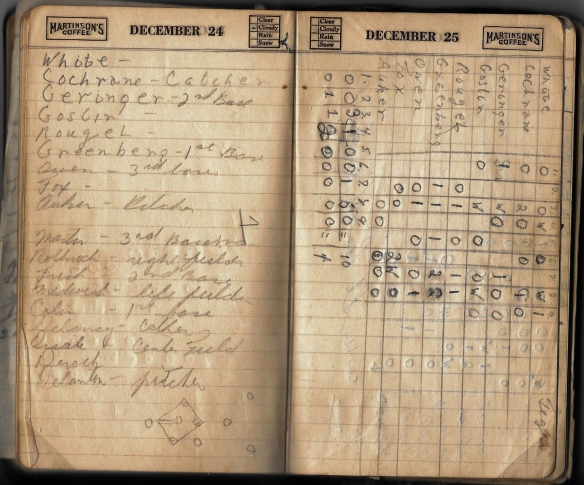
My uncle also must have liked baseball because he kept a box score from a game in the notebook. Being a baseball fan, I was determined to figure out not only what teams these were, but what game it was:
After studying the names on team listed on top I realized that it was the Detroit Tigers, probably around 1935. As soon as I saw Greenberg, I knew it had to be Hank Greenberg and thus the Tigers. After all, how many baseball players have there been named Greenberg?

English: 1934 Goudey baseball card of Henry “Hank” Greenberg of the Detroit Tigers #62. PD-not-renewed. (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
The team at the bottom took some more digging because my uncle’s spelling was, shall we say creative? But the Deroch was a big clue—I assumed it was Leo Durocher, and once I looked up his career and saw that in 1935 he was playing on the St. Louis Cardinals with a catcher named Bill Delancey, an infielder named Collins and another named Frisch, I knew I had found the right team.

English: 1933 Goudey baseball card of Leo Durocher of the Cincinnati Reds #147. PD-not-renewed (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
But the National League Cardinals wouldn’t have been playing the American League Tigers in 1935 unless they were in the World Series (oh, for the days before endless post-season playoffs and in-season interleague play!). So this couldn’t be 1935 because the Tigers played the Cubs in the 1935 World Series. After a bit more research, I concluded that this was a game from the 1934 World Series between the St. Louis Cardinals and the Detroit Tigers.
http://www.gettyimages.com/detail/573856419
http://www.gettyimages.com/detail/573867867
Since my uncle recorded the final score of the game he was following (presumably on the radio) as 10-4, it wasn’t hard to find out which game this was from the 1934 World Series: Game 4 on October 6, 1934, at Sportsmen’s Park in St. Louis. Here is a link to the box score of that game as recorded by the Baseball-Reference website. The Tigers evened the series 2-2 by winning that game and then won Game 5 to go up 3-2 in the Series, but badly lost Games 6 and 7 to lose the Series. I wonder which team my uncle, a boy from Brooklyn, was rooting for. Perhaps the one with the first Jewish player elected to the Baseball Hall of Fame?
Finally, there are a few short notes from my mother, the baby in the family. Here she wrote about her big brother teasing her:
My brother is such a pest he calls me all sorts [?] of names for instance fatso, horse, baby and so many and I call him names to.” I guess my uncle was always a tease—he certainly was as an adult also!
I wonder how much later she wrote the comment that follows: “When I look at this now I think it silly. It is childish.”
When she was eleven, she wrote about a favorite teacher, Mrs. Alice Handelsman, who was “just like a mother” to her class, and her boyfriend Myron. On his birthday in the calendar, she listed a favorite cousin, Sanford (or Sandy), Leo and Mildred Ressler’s son; my mother to this day talks about what a beautiful little boy he was and how kind he was to my grandmother.
What a gift this little book from 1930 has turned out to be. It gives me a snapshot into the childhood of my mother and her siblings and some insights into my grandfather as well. He was obviously a very careful man when it came to money, recording so painstakingly his income and his expenses. These were the Depression years, and my grandfather worked as a driver for a milk company. My grandparents were not poverty stricken, but they lived from paycheck to paycheck and for many years lived in a small apartment in Brooklyn and then a one bedroom apartment in Parkchester when my mother was a teenager and her siblings were married and out of the house. My grandfather worked the night shift for the milk company, and my mother would share the bed with my grandmother until my grandfather got home in the morning and she got up for school. But my mother says she never thought of herself as poor because she always had food and clothing and a roof over her head.
We take so much for granted today with our cars and houses and televisions and computers and smartphones. We throw everything away and litter our landfills with our junk. Our children and grandchildren have iPads and scooters and bikes and more toys and books than all the children in one tenement building in Brooklyn combined had back in the 1930s. But my mother and her siblings had their imaginations and their friends and their teachers and their families. And this one little notebook gives us a peak into how they entertained themselves and how they lived together as a family. It, like my aunt’s baby book, is a real treasure.